Search results
Search for "inclusion complex" in Full Text gives 100 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Cyclodextrins permeabilize DPPC liposome membranes: a focus on cholesterol content, cyclodextrin type, and concentration
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1570–1579, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.115

- ) was able to form two types of soluble complexes, with molar ratios of 1:1 and 1:2 (CHOL/DOM-β-CD). The latter (1:2 inclusion complex) occurred much more easily than that of the 1:1 complex showing a much higher equilibrium constant. At low CDs concentration, the formation of the 1:1 inclusion complex
- dominated with low equilibrium constant (109 M−1) suggesting that the unstable complex would rapidly decompose into its components. With time elapsing and with increasing CDs concentration, the 1:1 inclusion complex was transformed into the more stable 1:2 complex with greater equilibrium constant (5.68
CO2 complexation with cyclodextrins
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1021–1027, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.78
- split over two positions yielding in total 5.75 mol of water per CO2. The hydration is similar to that of native α-CD [13] and that of the krypton inclusion complex which has 5.28 water/Kr [14]. The CO2 molecule refines with an optimal occupancy of 0.84 and linear geometry (178.2(6)o) with C–O bond
Cyclodextrins as building blocks for new materials
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 889–891, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.66

- containing CDs. Three clinical trials have demonstrated the use of CDs in the treatment of COVID-19. Two of them use the sulfobutyl ether β-CD/remdesivir inclusion complex and the third applies the α-CD/sulforaphane inclusion complex called Sulforadex® [6]. The approved Janssen vaccine against SARS-CoV-2
A fluorescent probe for detection of Hg2+ ions constructed by tetramethyl cucurbit[6]uril and 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethene
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 864–872, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.63

- that TMeQ[6] and G form an inclusion complex with a host–guest ratio of 1:1 and the equilibrium association constant (Ka) was 2.494 × 104 M−1. The G@TMeQ[6] fluorescent probe can sensitively recognize Hg2+ ions by fluorescence enhancement. The linear range is 0.33 × 10−5–1.65 × 10−5 mol·L−1, R2
- that a G and TMeQ[6] inclusion complex is formed with a 1:1 stoichiometry. Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) analysis The association constant and thermodynamic parameters of the host–guest interaction between G and TMeQ[6] can be obtained using ITC. At 25 °C, a neutral aqueous solution of TMeQ[6
- structure of the inclusion complex formed by TMeQ[6] and G was obtained using X-ray single-crystal diffraction analysis. The crystal data and parameters are shown in Table 2. The single-crystal structure determination shows that the inclusion complex crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system, with the
pH-Responsive fluorescent supramolecular nanoparticles based on tetraphenylethylene-labelled chitosan and a six-fold carboxylated tribenzotriquinacene
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 635–645, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.45

- value when the concentration of CS-TPE-2% was 48 µg/mL, where a simple inclusion complex formed between TBTQ-C6 and CS-TPE-2%. As a result, the optimal mixing ratio for the formation of TBTQ-C6/CS-TPE-2% supra-amphiphilic assembly is 0.10 mM TBTQ-C6 + 48 µg/mL CS-TPE-2%. Analogously, the optimal mixing
Discrimination of β-cyclodextrin/hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) oil/flavonoid glycoside and flavonolignan ternary complexes by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy coupled with principal component analysis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 380–398, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.30
- cheap method for the evaluation of quality and similarity/characteristics of these new types of cyclodextrin-based ternary complexes having enhanced properties and stability. Keywords: antioxidant; cyclodextrin; flavonoid; hazelnut vegetable oil; ternary supramolecular inclusion complex; Introduction
- the co-precipitation from a saturated solution. The peony oil content in the complex was almost 26%, with a high ratio of unsaturated FA glycerides of ≈90% [20]. In a very recent study, perilla (Perilla frutescens (L.) Britton) seed oil was complexed by γ-CD and the inclusion complex was used for
CuAAC-inspired synthesis of 1,2,3-triazole-bridged porphyrin conjugates: an overview
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 349–379, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.29
- 126, it was used to form water-soluble porphyrin nanospheres by self-inclusion complex formation in water. Tritriazole-bridged porphyrin system This section contains the synthesis of porphyrin conjugates having three 1,2,3-triazole groups as linkers. In 2012, Beletskaya and co-workers [55] described
- , Jayawickramarajah and co-workers [69] synthesized a water-soluble porphyrin-fullerene (C60) nanorod through the formation of an inclusion complex between an octa(permethylated-β-CD)-Zn-porphyrin 174 and a pristine C60. For the construction of the nanorod, porphyrin 174 was first obtained in 65% yield by a Cu(I
Inclusion complexes of the steroid hormones 17β-estradiol and progesterone with β- and γ-cyclodextrin hosts: syntheses, X-ray structures, thermal analyses and API solubility enhancements
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1749–1762, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.184
- cm3·min−1. All DSC experiments were terminated prior to the decomposition of each sample. Solubility analysis by gravimetric increments A gravimetric solubility approach was used involving the addition of small, accurately pre-weighed incremental amounts of a given CD inclusion complex (total mass
- approximately 30 mg each) into a vial containing 3 cm3 of water. A visual estimation of the solubility was established after the final suspension was stirred for 72 hours at 27 °C. This procedure ensured that a very narrow solubility range was spanned by the penultimate and final incremental CD inclusion
- complex additions, the final amount resulting in saturation of the solution. The apparatus involved a Radleys Standard stirring hotplate with a 2.5 cm high vial supporting stand attached to it. The vials were placed on the stand in a circle at a radius of 4 cm from the centre, and the solutions were
Preparation of β-cyclodextrin-based dimers with selectively methylated rims and their use for solubilization of tetracene
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1596–1606, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.170
- effective values for the sum of all interaction steps. Although from the sole ITC experiment, the formation of tetracene inclusion complex with CDs can't be affirmed, the observed stoichiometry favors this hypothesis. Additionally, the binding strength in terms of Ka (M−1) well matches the solubility
Cyclodextrin-based Schiff base pro-fragrances: Synthesis and release studies
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1346–1354, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.140
- hydrophilic outer surface and hydrophobic cavity. This cavity can encapsulate another lipophilic guest molecule and thus form an inclusion complex [3][4]. This phenomenon is reversible and leads to an equilibrium between encapsulated and free guest. A staggering number of inclusion complexes of CDs with
Tetraphenylethylene-embedded pillar[5]arene-based orthogonal self-assembly for efficient photocatalysis in water
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 429–437, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.45

- G guest molecule were involved in the inclusion complex and further self-assembled to form worm-like supramolecular nanostructures, which displayed an AIE effect via restricted phenyl-ring rotation of m-TPEWP5. After that, the negative EsY acceptor was loaded on the positively charged surface of the
1,2-Naphthoquinone-4-sulfonic acid salts in organic synthesis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 53–69, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.5
- recognition of cholylglycine, which is a combination of cholic acid and glycine. The β-cyclodextrin/graphene oxide composite forms an inclusion complex with a β-NQS guest. The amino group of cholylglycine can bind to β-NQS by a nucleophilic substitution reaction, resulting in a decrease in the electrochemical
Host–guest interaction and properties of cucurbit[8]uril with chloramphenicol
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2832–2839, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.194
- Q[8] formed a 1:1 inclusion complex (CPE@Q[8]) with an inclusion constant of 5.474 × 105 L/mol. The intervention of Q[8] did not affect the stability of CPE, but obviously reduced the release rate of CPE in artificial gastric and intestinal juice; Q[8] has a slow-release effect on CPE. The
- in water and has a bitter taste. Upon forming an inclusion complex with cyclodextrin, the solubility and bitter taste of CPE can be improved [4][5]. Ramesh Gannimani et al. [6] reported that the inclusion complex of cyclodextrin and CPE loaded silver nanoparticles possessed stronger antibacterial
- and carbon atoms and the cavity has a certain degree of hydrophobicity that can form a stable host–guest inclusion complex with a guest molecule via non-bonding interactions, such as hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces and ionic dipoles [21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28]. It has been proved that
Host–guest interaction of cucurbit[8]uril with oroxin A and its effect on the properties of oroxin A
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2332–2337, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.194

- the inclusion compound with Q[8]. Keywords: cucurbit[8]uril; host–guest interaction; inclusion complex; oroxin A; properties; Introduction Cucurbit[n]urils (Q[n]s) are a family of macrocyclic cage compounds synthesized by the condensation of glycoluril and formaldehyde in a strong acidic solution [1
- in the case of an excess of OA, the port interactions and inclusion interactions of OA andQ[8] can exist simultaneously. To further determine the host–guest ratio of the inclusion complex formed by Q[8] and OA, their interaction was investigated using UV–visible absorption spectroscopy via a molar
- mode (Figure 3B). Figure 4 shows the IR spectra recorded for Q[8] (a), OA (b), a physical mixture of Q[8] and OA (n(Q[8]):n(OA) = 1:1) (c) and the OA@Q[8] inclusion complex (d). Curve (c) contains characteristic peaks of curves (a) and (b) without interaction in the physical mixture. Comparing spectra
Mechanochemical green synthesis of hyper-crosslinked cyclodextrin polymers
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1554–1563, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.127

- were obtained only with βNS-CDI 1:8. Even in case of βNS-CDI 1:8, if treated for 8 h in H2O at 40 °C (0.40% N), presented a low amount (≈0) of reactive IM, therefore the reaction did not occur at all, leading only to an inclusion complex with the dyes, which could be easily removed through a PS
[3 + 2] Cycloaddition with photogenerated azomethine ylides in β-cyclodextrin
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1296–1304, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.110
- azomethyine ylides, giving formal 1,4 H-shifted products. Thus, in the presence of H2O, no cycloaddition products are anticipated. However, it should be probed if the [3 + 2] cycloaddition can compete with the 1,4 H-shift upon irradiation of an inclusion complex. Under our conditions, photodecarboxylation of
- of the phthalimide, which changed from a singlet to a multiplet (Figure S1 in Supporting Information File 1). The spectral changes are in accordance with the formation of an inclusion complex 2@β-CD, with the dynamics for the complexation faster than the NMR time-scale (millisecond). Nonlinear
- regression analysis of the chemical shifts depending on the β-CD concentration, to a complexation model with 1:1 stoichiometry, showed good correlation (Figure 2 and Figure S2 in Supporting Information File 1), with the stability constant for 2@β-CD K = 190 ± 50 M−1. Formation of the inclusion complex was
The interaction between cucurbit[8]uril and baicalein and the effect on baicalein properties
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 71–77, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.9
- corresponding properties of the inclusion complex were studied using 1H NMR, IR and UV–vis spectroscopy and DTA. The results showed that BALE forms an inclusion compound (1:1) with Q[8], and the properties of baicalein are changed by cucurbit[8]uril. Keywords: baicalein; cucurbit[8]uril; host–guest interaction
- ; inclusion complex; properties; Introduction Baicalein (5,6,7-trihydroxyflavonoid) has a molecular formula of C15H10O5 (BALE, Figure 1) and is a natural flavonoid found in the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi [1]. The compound displays pharmacological activity such as antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory
- compounds such as calixarenes, crown ethers and cyclodextrins, which can be used to form a stable inclusion complex with the drug, and improving the bioavailability of the drug [34][35]. Herein, we describe the results of the investigations of host–guest interactions between BALE and Q[8] in an aqueous
Reversible switching of arylazopyrazole within a metal–organic cage
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2398–2407, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.232

- switching to the Z isomer was accompanied by the release of one of the two guests from the cage and the formation of a 1:1 cage/Z-arylazopyrazole inclusion complex. DFT calculations suggest that this process involves a dramatic change in the conformation of the cage. Back-isomerization was induced with
- ; the strongest correlations were found between Ha and H1 and between Hc and H4 (Figure S20, Supporting Information File 1; note that the opposite was found for the E isomer, cf. Figure 2). Despite repeated efforts, we did not succeed in preparing crystals of the (Z-1)2 inclusion complex suitable for X
- –guest inclusion complex incorporating two molecules of arylazopyrazole was obtained in a quantitative yield. The complex was characterized by a series of NMR techniques, which showed that the resonances of the guest protons were upfield-shifted by up to 2.2 ppm. An antiparallel configuration of the
Synthesis of a [6]rotaxane with singly threaded γ-cyclodextrins as a single stereoisomer
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1829–1837, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.177

- . Although the hydrophobic biphenylene is expected to form a more stable inclusion complex with γ-CD due to a stronger hydrophobic effect, a structure with the γ-CD interlocking at the central biphenylene of 4R may not explain the non-equivalent chemical environments of the two termini. As discussed in the
Host–guest interactions in nor-seco-cucurbit[10]uril: novel guest-dependent molecular recognition and stereoisomerism
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1705–1711, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.166
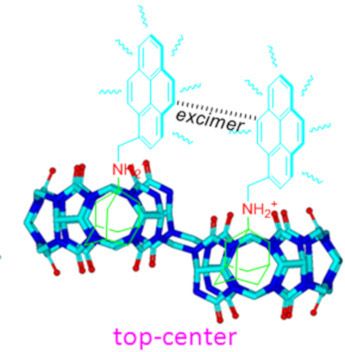
- and TΔS = −21.66 kJ·mol−1 for inclusion complex G1·host-1; ΔH = −65.77 kJ·mol−1 and TΔS = −26.46 kJ·mol−1 for the inclusion complex G2·host-1; ΔH = −39.01 kJ·mol−1 and TΔS = −1.02 kJ·mol−1 for the inclusion complex G1·host-2); while only the formation of the inclusion complexes of host-2 with G2 is
Host–guest interactions between p-sulfonatocalix[4]arene and p-sulfonatothiacalix[4]arene and group IA, IIA and f-block metal cations: a DFT/SMD study
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1321–1330, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.131

- anchoring points for the positively charged guests. Cation–π interactions between the monoatomic cations and p-sulfonatocalix[4]arene in water are supposed (but not proven) to take part in the inclusion complex formation [31]. Mendes et al. have carried out molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of association
- the SO3 belt (common structural unit for both molecules) which is far away from the structurally different methylene/sulfur bridges at the lower rim. Water solvation has great impact on the Gibbs energies of the complex formation. The process of inclusion complex formation in aqueous solution becomes
Precious metal-free molecular machines for solar thermal energy storage
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1096–1106, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.106

- constant was found to be K = 70 ± 15 M−1 which is in good correlation with the published data [22]. These results prompted us to identify the optimal Ba2+ concentration, necessary for a maximum degree of dye–Ba2+ inclusion complex formation. Obviously for a better complexation it is necessary to work with
Fabrication of supramolecular cyclodextrin–fullerene nonwovens by electrospinning
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 89–95, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.10

- introducing functional groups into the molecule directly. Among them, the formation of a 2:1 inclusion complex of γ-CD and C60 has been evaluated in various solvents such as water [21], toluene/water [22], DMSO [23], and DMF/water [24]. Although an impressive report that a 2:1 complex in water can be utilized
- realizes easy handling of inclusion complexation with guest molecules as well as electrospinning due to the much lower viscosity of the CD/HFIP solution. The formation of a 2:1 inclusion complex should not affect the solution properties (e.g., viscosity and solubility), but should provide electrospinning
- parameters similar to the case without the guest because the guest molecule is isolated from the solvent molecules by two γ-CD molecules. This is in contrast with the part of the guest molecule uncovered by γ-CD which may interact with the solvent molecules in the case of a 1:1 inclusion complex. Moreover
Synthesis of a water-soluble 2,2′-biphen[4]arene and its efficient complexation and sensitive fluorescence enhancement towards palmatine and berberine
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2236–2241, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.198

- compared with the free guest. Especially, the chemical shifts for the middle protons, H1–6, and H10–11, are larger than those for the ending H7–9. These results indicate that berberine was engulfed by the cavity of 2,2’-CBP4 to form a pseudorotaxane-type inclusion complex. Similar complexation-induced NMR
- changes were observed for the host–guest mixture of P and 2,2’-CBP4 (Supporting Information File 1, Figure S9), suggesting a similar binding mode of an inclusion complex. The host–guest encapsulation was then confirmed by 2D NOESY experiments, as shown in Figures S10 and S11, Supporting Information File 1
Efficient catenane synthesis by cucurbit[6]uril-mediated azide–alkyne cycloaddition
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 1846–1853, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.158

- Scheme 1. The secondary amines are designed to form ammoniums that will strongly bind to CB[6] through ion-dipole interactions under aqueous acidic conditions. Upon formation of the inclusion complex with CB[6], the azide and alkyne functionalities inside the CB[6] cavity will be placed in close
- formed that indicated CB[6] dissolution and formation of the inclusion complex. One equivalent of DN-CC was added and the mixture was further heated at 70 °C. LC–MS analysis of the reaction mixture showed that the building blocks were completely consumed after one hour of heating, and that the crude
- known to form a stable inclusion complex with the BP unit due to hydrophobic effects (Ka ≈ 7 × 103 M−1 in D2O) [26] (Scheme 4). To our delight, a [4]catenane (Cat-11) was obtained in 60% yield along with 30% of Cat-3. Of note, due to a much weaker binding between the 1,5-dioxynaphthalene unit and β-CD





























































































































































































































































